Collections in Java
- FRAMEWORKS
- ADVANTAGES OF JAVA COLLECTION FRAMEWORK
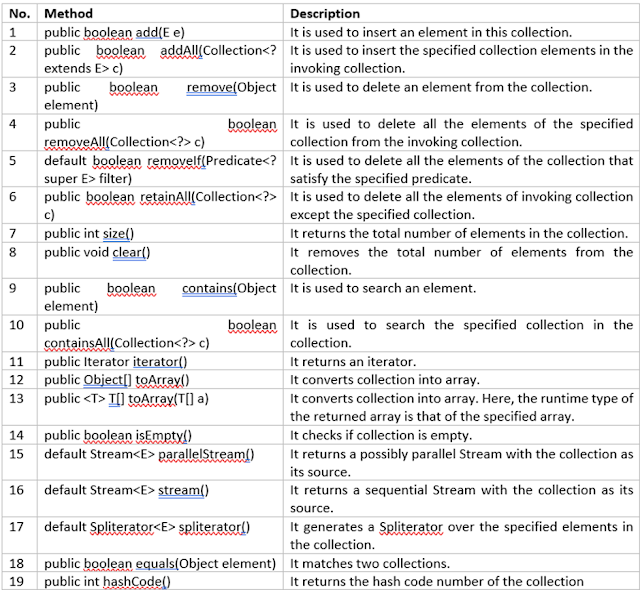
- METHODS OF COLLECTION INTERFACE
- LINKED LIST
- VECTOR
- STACK
- QUEUE INTERFACE
- SET INTERFACE
- CLASSES THAT IMPLEMENT THE SET INTERFACE( HARSH SET, SORTED SET, MAP, ETC)
Java's Collection framework may be used to store and manage collections of objects.
Java
Collections may be used for data operations such as sorting, searching,
inserting, modifying, and removing. In Java, an object collection is called a
collection. The Java Collection foundation includes classes and interfaces
including Vector, LinkedList, Priority Queue, HashSet, LinkedHashSet, and
TreeSet.
Framework in Java
An
architecture that has already been created for a group of classes and
interfaces is called a framework. It is not necessary to define a framework to add a new class or function. But with a perfect object-oriented
design, there is always a framework with classes in it, so every class does the
same job.
Java's
unique collection structure is required
Arrays,
vectors, and hash tables were the usual Java ways for objects (or collections) before
the introduction of the collection framework (or JDK 1.2). All of these
collections lacked a single, cohesive user interface. As a result, even while
every collection aims to achieve the same general objective, each collection's
implementation was decided upon independently of the others. Not to mention how
hard it is for users to remember the distinct constructors, functions, and
syntax of every collection class.
A nice
example of this is the procedure for adding an element and a vector to a hash
table.
Let's
see an example here:
// why collection framework was needed
The
Array, Vector, and Hash table collections had a standard member interface, which
made it hard for programmers to design algorithms that could manage several types
of collections. Another disadvantage is that since the majority of the 'Vector'
methods are final, therefore we can't modify the 'Vector' class to create an
equivalent collection. As a result, the Java development team created the
Collection Framework in JDK 1.2 as a common interface to handle the
aforementioned problems; this framework was used to standardize both the hash
table and the outdated vectors.
Advantages of Java collection framework
Since
the aforementioned disadvantages stem from the absence of a collecting
framework, the following are advantages of having one.
When
all classes that implement an application programming interface (API) utilize
the same set of methods, that API is said to be consistent. This comprises,
among other things, Set, LinkedList, Vector, and ArrayList.
reduces
the developer's workload on the code by letting him focus on using the
collection as efficiently as can rather than thinking about how it was
designed. This successfully implements the core concept or features of
object-oriented programming, which is sometimes referred to as abstraction.
Enhances
the effectiveness and caliber of the program Since algorithms and data
structures are supplied in a useful and efficient way—the programmer is not
performing their job here—performance is enhanced. It is essential to think
about how best to use a certain data structure. All he needs to do is employ
the best implementation to significantly increase the efficiency of his
algorithm or program.
Collection
interface
The
collection interface is followed by every class that comprises the collection
framework. It spells out how each set is to be done. Stated differently, a
collection interface creates the basis upon which the entire framework is
built.
Every
subclass implements many of the methods available in the collection interface.
void clean (), Boolean add All (Collection c), and Object obj are a few of these
methods.
List interface
The
list interface is a subset of the overall interface. These blocks allow us to
store an ordered collection of items in a list-type data structure. It can hold
several values in storage.
The
List interface is implemented by the classes ArrayList, LinkedList, Vector, and
Stack. One cannot construct the List interface without first using it.
- List <data-type> list1= new ArrayList();
- List <data-type> list2 = new LinkedList();
- List <data-type> list3 = new Vector();
- List <data-type> list4 = new Stack();
Iterable interface
The
primary interface via which all collection classes communicate with one another
is the Iterable interface. All Aggregate subclasses implement the Iterable
interface as the aggregate interface is an extension of the Iterable interface.
It has
just one abstract method. in other words,
Iterator<T> iterator ()
Iterator interface
The
Iterator UI provides the ability to iterate elements forward only.
Iterator UI Methods The Iterator UI has only three methods. They are:
Array list
We can
access dynamic arrays using Java thanks to the ArrayList class. It may operate
more slowly than traditional arrays, but in high-traffic scenarios, it can be
helpful. An ArrayList's count automatically increases as new members are added,
and it automatically decreases when elements are removed. Java ArrayList allows
for random access to the list. Older data types that are incompatible with
ArrayList include char, int, and so on. In these cases, you need a wrapper
class.
Let's
understand ArrayList with the below example.
// Below Java program to show how the ArrayList works
Linked list
One technique to build the linear
LinkedList data structure is with the LinkedList class. It handles each element
as an individual object with data and an address component, and stores items in
non-contiguous places. The parts are linked via pointers and addresses. A node
is an individual component.
Let's use the following example to better understand Linked Lists.
let us
try with an example:
// Below program to show the working of LinkedList in Java
Vector
In Java, we may access dynamic
arrays via a vector. It may work slower than regular arrays, but it may be
useful for systems that need to manipulate arrays extensively. The
implementation of this is the same as that of ArrayList. But the main
distinction between an array list and a vector is that the former is
non-synchronized while the latter is.
Let's use an example to better grasp the Vector.
// Below
program to shows the working of Vector in Java
Stack
The stack data structure is
implemented and modeled by the Stack class. The last-in, first-out policy
governs the class. This class additionally has the empty, search, and peek
methods in addition to the regular push and pop methods. Another name for the
class is the Vector subclass.
Let's use an example to better
grasp the stack.
// Below
program to shows the working of a stack in Java
Queue interface
The
queue interface follows the First In First Out (FIFO) protocol, much like a
real queue would. This interface can handle all of the components if the order
is important. Every time we try to book a ticket, we witness this in action
because there are relatively few available. As a result, the ticket will be
given to the person whose request is next in line. There are several classes
available, including Array-Deque and Priority-Queue. Since all of these
subclasses implement Queue, if we want or need then we can use any of them to
construct a Queue object.
- Queue<String> q1 = new PriorityQueue();
- Queue<String> q2 = new ArrayDeque();
Priority queue
When processing
items depending on their priority, a priority queue is used. The Priority-Queue
class is used when processing the queue's items based on priority is necessary,
even if it is widely known that the queue runs on a First-In, First-Out basis.
Priority-Queue is fundamentally a priority queue. The priority queue items are
sorted using either the Comparator that is specified when the queue is
established or by natural order, depending on which constructor was used.
By
understating the below code we can also understand the priority queue:
// priority queue in Java
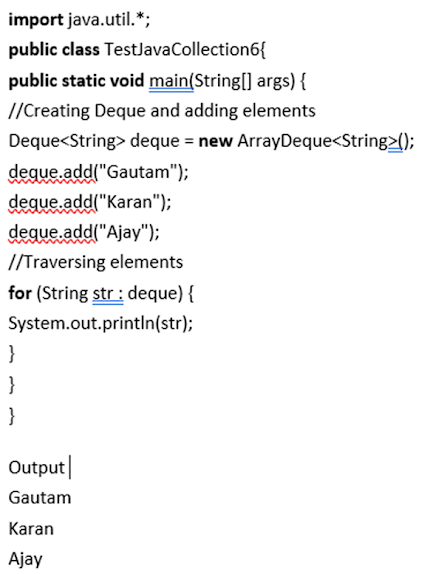
Deque interface
In
this instance, the Queue data structure has undergone some modification. Double
queues are another type of data structure that is similar to a queue, let us
add and delete bits from both ends. Compared to the queue interface, this
interface is superior. The Array-Deque class makes use of this interface. We may
create a deque object by implementing the Deque interface with the help of the
Array-Deque class.
Deque d = new ArrayDeque();
Array deque
Array-Deque
is a class that complies with the Deque specification. Deque's use is made
easier by this. In contrast to a queue, we can add and remove things
from both ends.
There
is no size restriction for Array-Deque, and it is quicker than ArrayList and
Stack.
Let’s look at the below code example.
Set interface
An array is a non-recursive set of items that prevents duplicate data
from being stored. We use this collection when we wish to preserve only unique
things in our collection and not any that overlap. This set interface is used
by numerous classes, such as LinkedHashSet, TreeSet, HashSet, and many more.
Since all of these classes implement a set, you may use any of them to create a
set object.
For example.
Set<data-type> s1 = new HashSet<data-type>();
Set<data-type> s2 = new LinkedHashSet<data-type>();
Set<data-type> s3 = new TreeSet<data-type>();
Classes that implement the set interface
Harsh-set
The HashSet class, a private variant of the
hash-table data structure, is utilized inside. It cannot be guaranteed that
elements that are addable to a hash set will be added in a predetermined
sequence. Every item is placed based on its hash code. Additionally, NULL
objects are allowed in this class. To help you understand HashSet, consider
this example.
// working of a HashSet
Sorted set interface
This interface and the fixed interface have several things in common. The only way this interface is different is that it
offers additional techniques for maintaining element order. The Sorted-Set
interface extends the Set interface to provide a more convenient way to handle
sorted data. Without the TreeSet class, you cannot construct this interface.
Since this class is an implementation of Sorted-Set, Sorted-Set instances can be
created using it.
SortedSet<data-type> set = new TreeSet();
Tree
set
What the TreeSet class uses is a storage tree. The array will use the elements' natural order to maintain order whether or not an explicit comparator is provided. If the set interface is incompatible with its peers, it cannot be implemented correctly. It can also be purchased with a Comparator that is meant to be delivered at a certain construction time, depending on the builder. An example will help you better understand TreeSet.
Map interface
A map is one tool for organizing data that lets you
work with key-value pairs. This interface does not support duplicate keys since
a single key cannot have multiple mappings. Nevertheless, duplicate values can
exist for separate keys. The map comes in helpful when the data is already
available and we want to use the key to conduct actions. Many classes implement
this Map interface, such as HashMap, Tree-Map, and others. All of these classes
implement Map, thus we can use any of them to generate a Map object.
Map<T> hm = new HashMap<> ();Map<T> tm = new TreeMap<> ();Where T is the type of the object
Hash map
HashMap offers a basic Java implementation of the map interface. Data is stored using pair notation (key, value). To retrieve the value of a hash map, we must know its key. HashMap employs the hashing method. Hashing may be used to break up large strings into smaller ones that nonetheless represent the same string for more effective indexing and search operations. HashMap is also used internally by HashSet. Let's examine HashMap as an illustration.















No comments:
Post a Comment